Diphallia: An Overview, Occurrence, and Impact of Having Two Penises
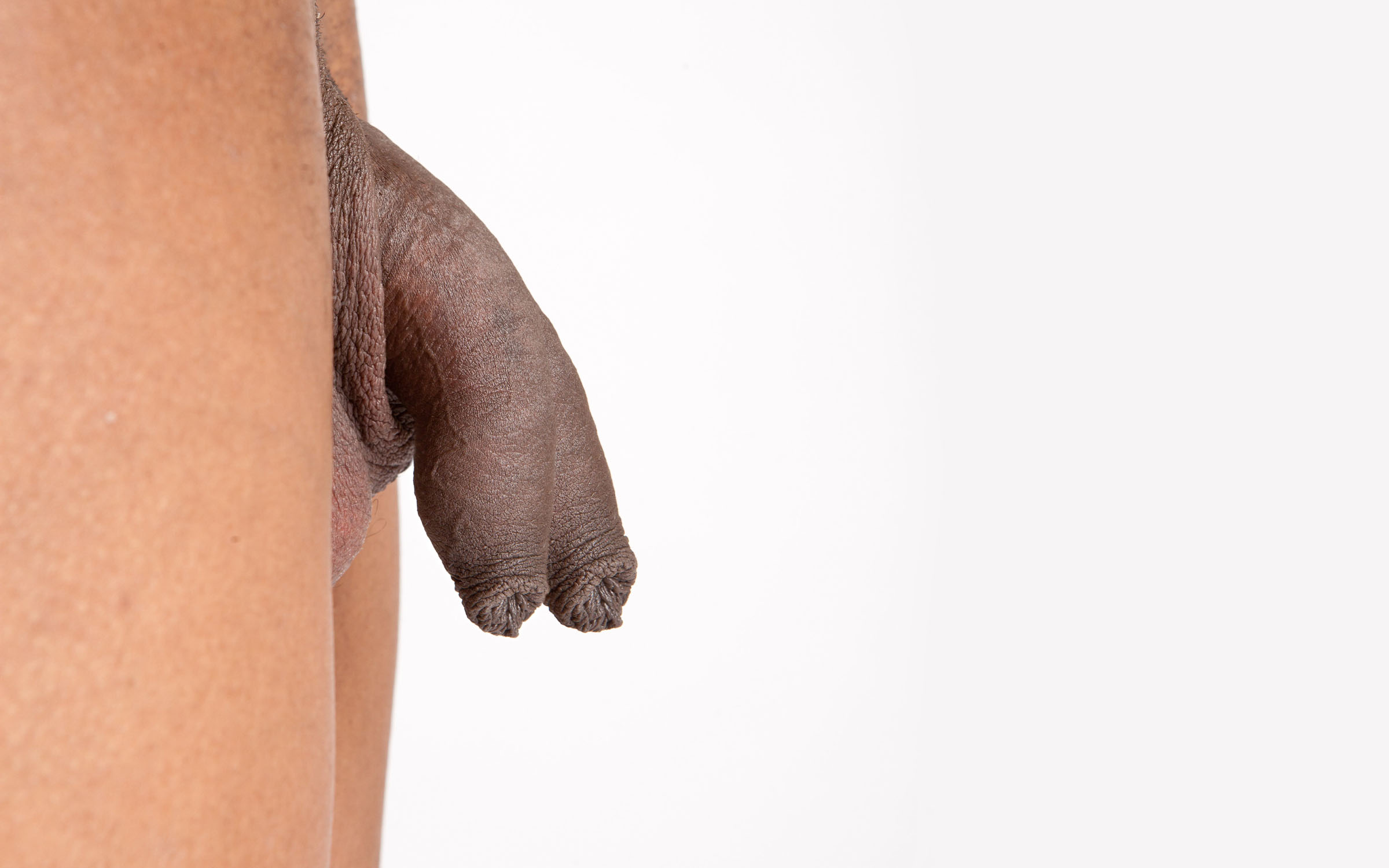

Diphallia is an extremely rare medical condition, also known as penile duplication, in which a male is born with two penises. The term "diphallia" originates from Greek, with "di" meaning "two," and "phallus" meaning "penis."
What is Diphallia?
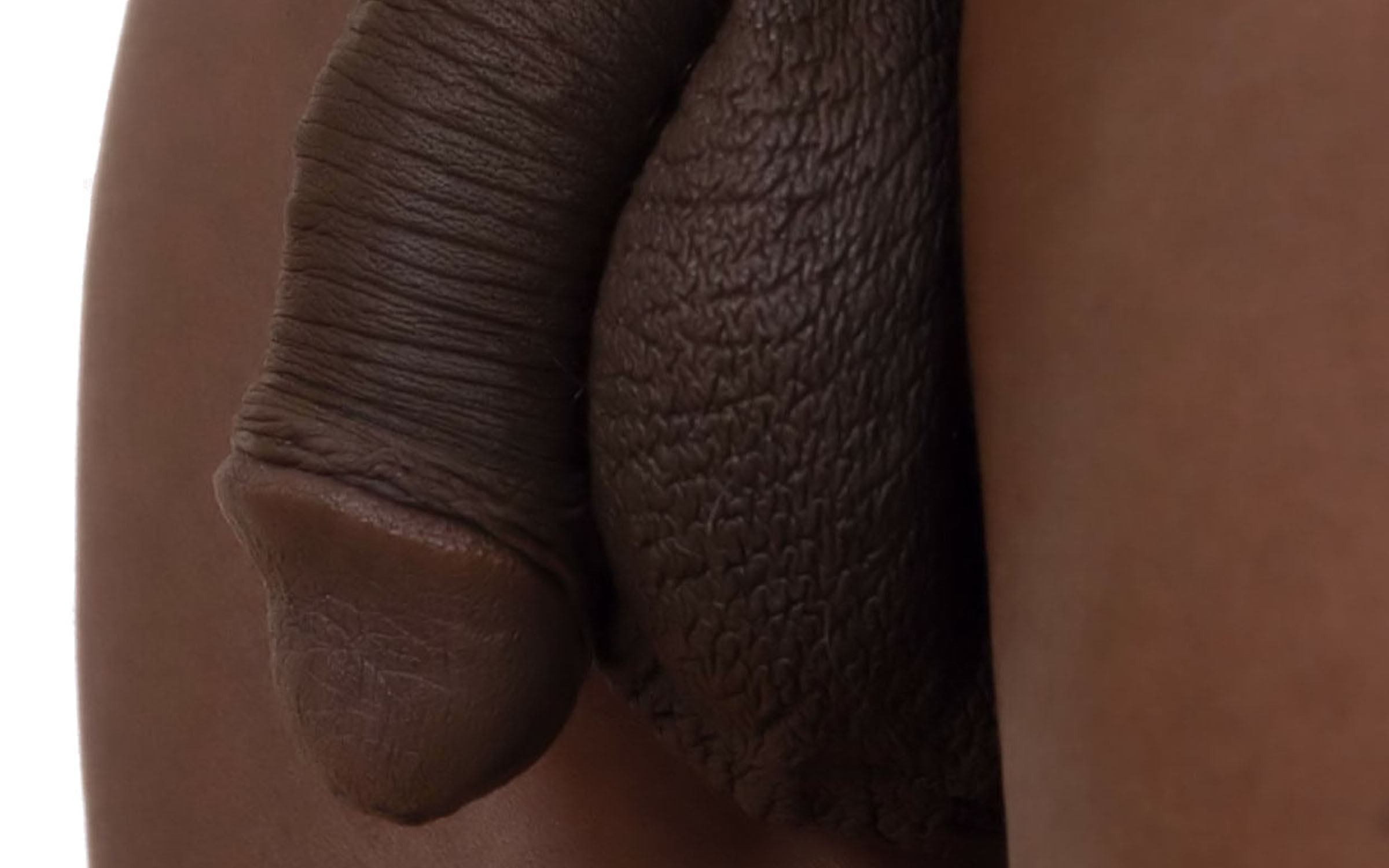
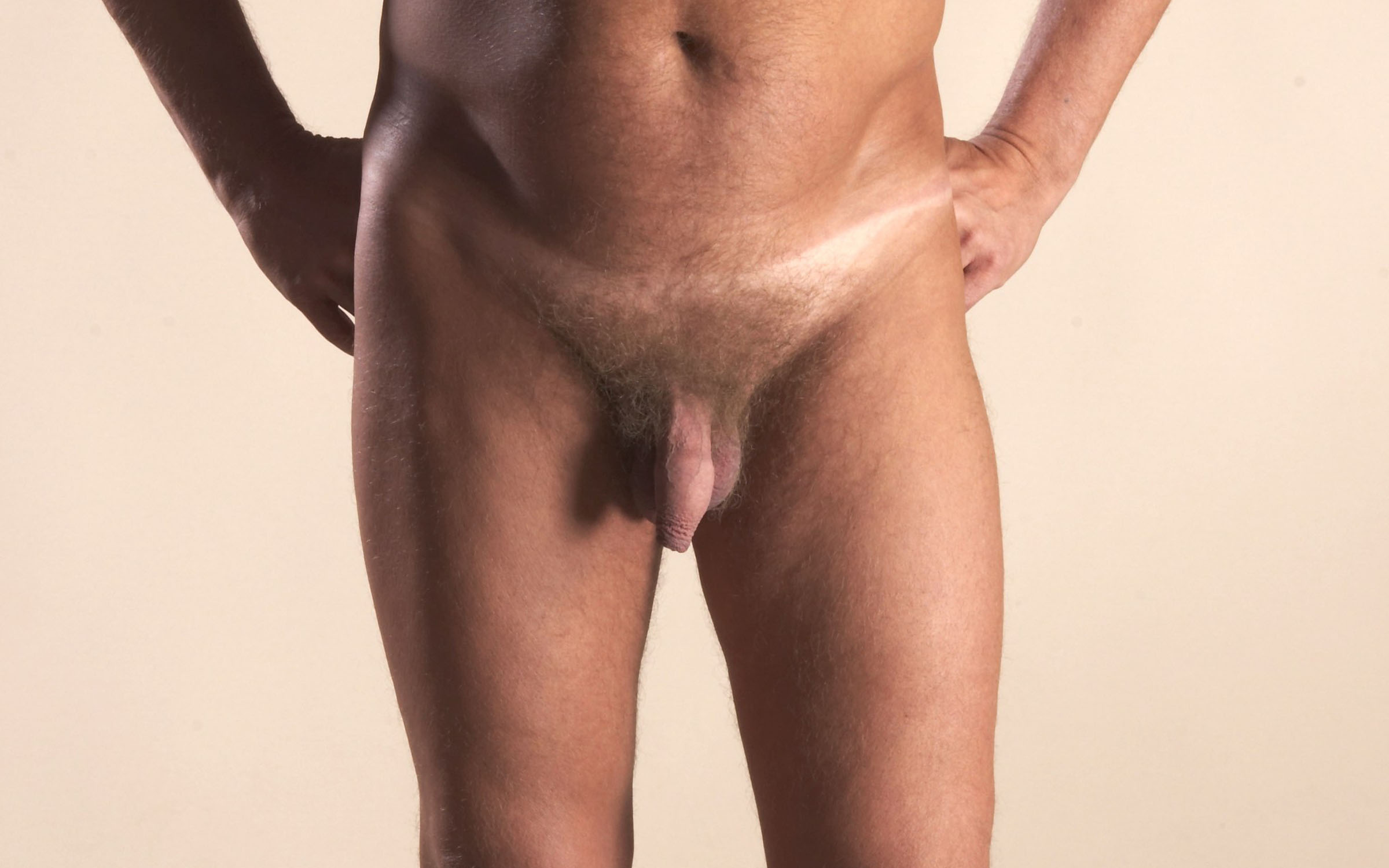
Diphallia is a congenital anomaly, meaning it's present at birth, and it's characterized by the presence of two penises. The penises may be side by side or one above the other. Depending on the individual, both penises may be fully functional, or only one may function normally. In some cases, neither may be functional for sexual activity or urination.
The severity and presentation of diphallia can vary greatly from individual to individual. The condition can exist in three forms:
- Diphallia of glans: In this form, the duplication is only present in the glans, or the tip of the penis.
- Partial diphallia: In partial diphallia, there is a duplication of part of the penis.
- Complete diphallia: This is the most severe form where there are two separate penises, each with a urethra.
How does Diphallia Occur?
Diphallia is thought to occur as a result of an error during embryonic development, specifically during the 23rd to 25th day of gestation. This is the period when the penis starts to form in a male fetus. It's believed that an excess of a signaling protein called "sonic hedgehog homolog" (SHH) is a factor in this anomaly. The SHH protein plays a critical role in the organization and growth of many body tissues during embryonic development.
Despite these findings, the exact cause of diphallia remains unknown. It is not associated with the actions or health of the mother during pregnancy and does not appear to have a genetic link, meaning it is not likely to be inherited.
Impact on Men with Diphallia
For men with diphallia, the condition can bring various medical, psychological, and social challenges. Medical issues often co-occur with diphallia, including spina bifida, anorectal, urethral, and bladder anomalies. Men with diphallia may also face a higher risk of kidney abnormalities and other organ malformations.
Psychologically, men with diphallia may struggle with issues surrounding self-image and sexual identity. They may also experience difficulties in establishing intimate relationships due to the unique nature of their condition.
From a societal perspective, the rarity and stigma associated with the condition can make it challenging for individuals to navigate everyday life. There is a need for increased awareness and understanding of this condition to lessen social stigma and improve support for affected individuals.
Estimated Prevalence of Diphallia
It is difficult to accurately determine the prevalence of diphallia due to its rarity and the possible underreporting of cases. However, estimates can be derived from medical literature and registry data. Here's a brief data table giving a rough estimate:
|
Country |
Estimated Cases (per million male births) |
Total Estimated Cases (based on population data as of 2021) |
|
United States |
0.5 - 1 |
75 - 150 |
|
United Kingdom |
0.5 - 1 |
15 - 30 |
|
India |
0.5 - 1 |
700 - 1400 |
|
China |
0.5 - 1 |
800 - 1600 |
|
Worldwide |
0.5 - 1 |
3,900 - 7,800 |
Please note that these are approximations and the actual numbers might differ.
Conclusion
Diphallia is a rare and complex condition that demands comprehensive and sensitive medical attention to adequately address both physical and mental health aspects. Further research is needed to better understand the condition and improve treatments and support for affected individuals. Increased awareness and understanding of the condition can also help reduce societal stigma and support the wellbeing of those living with diphallia.